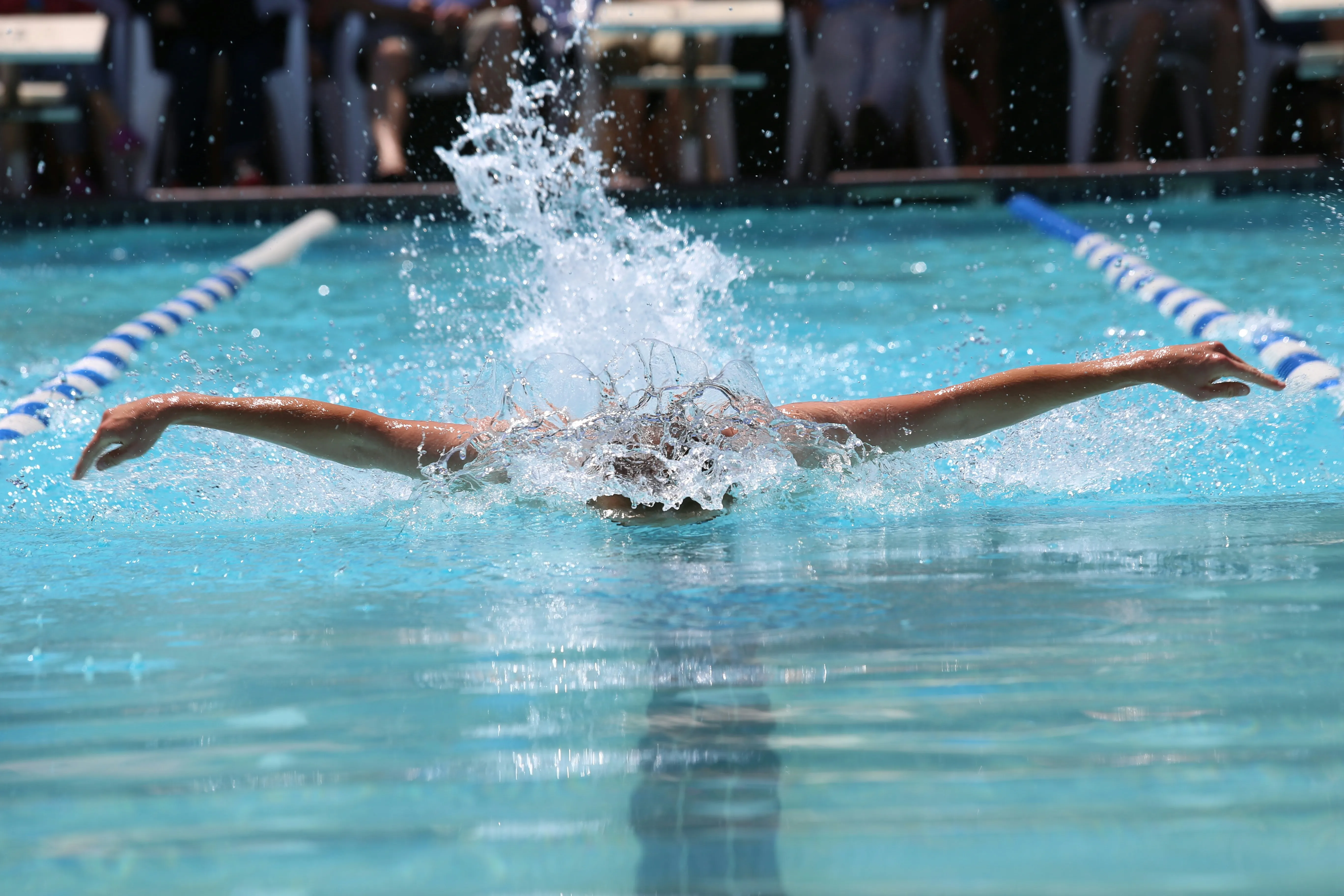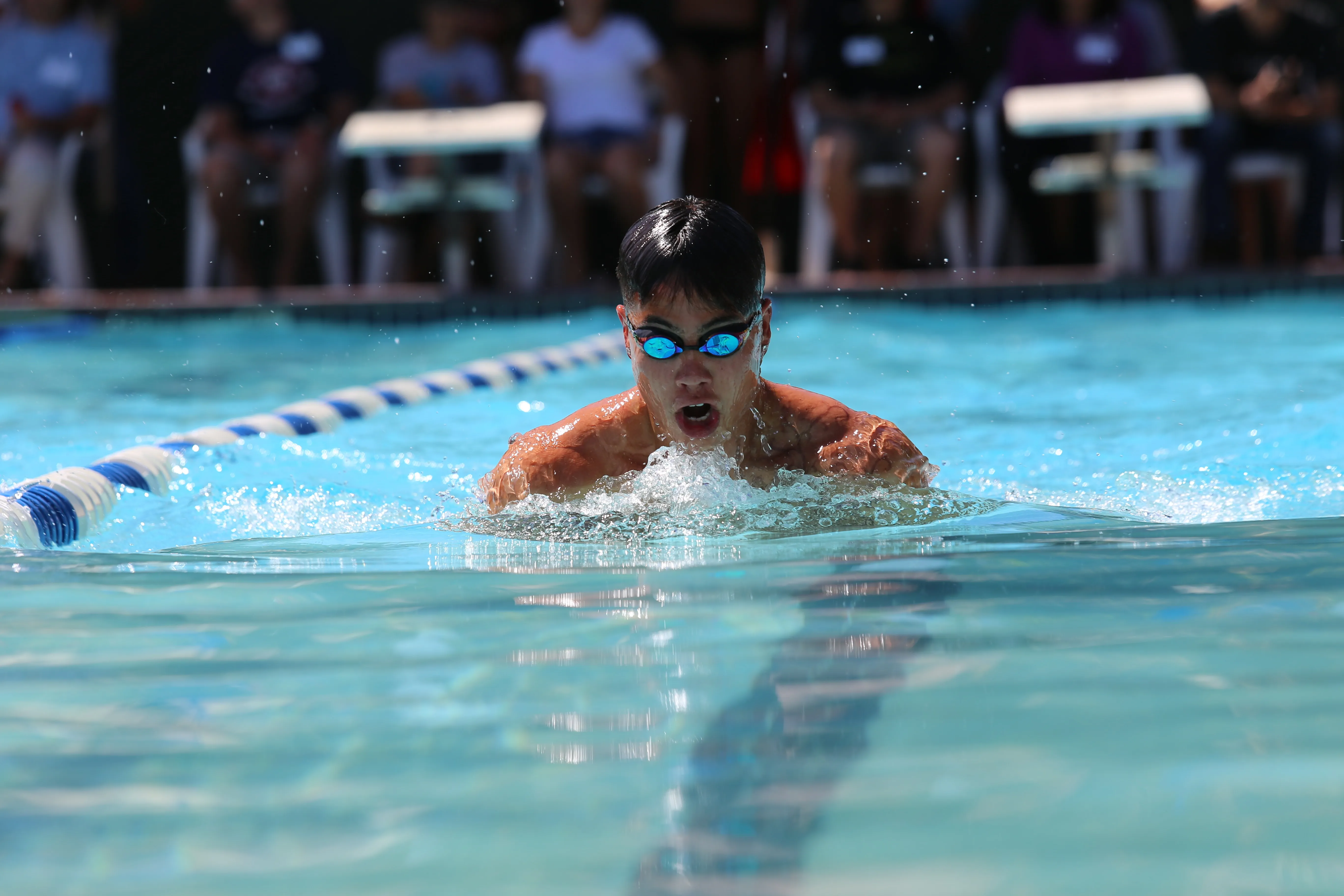The Science of Swimming: How Water Resistance Shapes Your Body

Swimming is a unique sport that combines the power of water with human physiology to offer a comprehensive workout. But how exactly does swimming shape and condition your body? What are the science and health benefits behind this popular water sport? This guide will take a deep dive into the fascinating science of swimming and explore how water resistance plays a crucial role in shaping your body.
Understanding Water Resistance
Water resistance is a key factor that makes swimming different from land-based exercises. It works on the principle of drag forces. When you swim, you're continuously pushing against water, which provides resistance in all directions. This resistance, up to 14 times greater than air, forces your body to work harder, enhancing the workout you get from each stroke.
The Science of Swimming Strokes
Each swimming stroke involves a complex interplay of physics and body mechanics. Let's explore the science of swimming through the four major strokes:
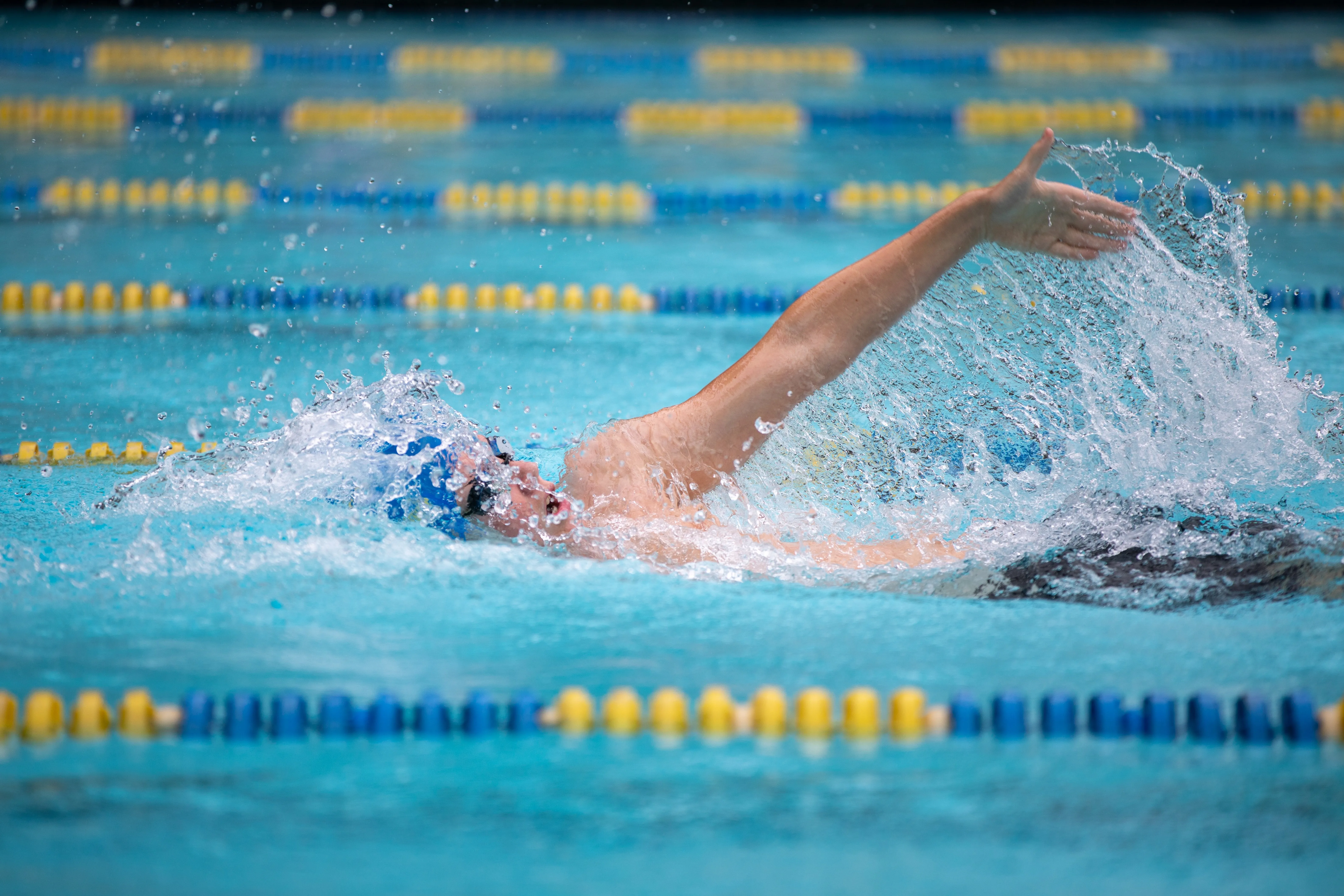
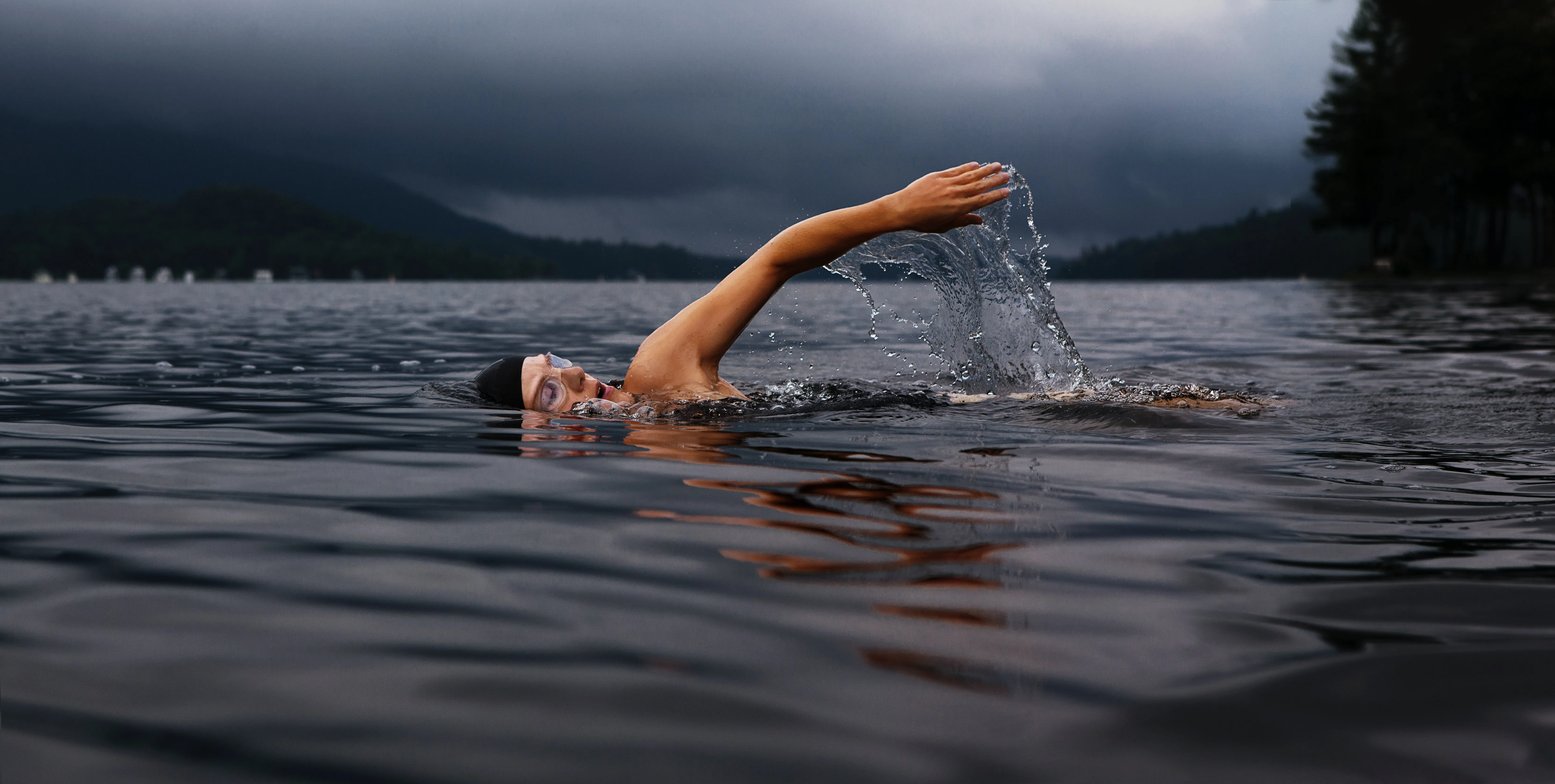
1. Freestyle: The freestyle or front crawl is the most efficient stroke, primarily working the shoulders, back, and leg muscles. The key to speed lies in reducing drag through a streamlined body position and efficient kick.
2. Backstroke: Similar to freestyle but performed on the back, this stroke employs the same flutter kick and alternate arm strokes. The challenge lies in maintaining a straight path without visual guidance.
3. Breaststroke: This stroke involves simultaneous circular arm motions and a whip kick. Despite its slower speed, breaststroke provides an excellent full-body workout and improves flexibility.
4. Butterfly: The most physically demanding stroke, butterfly involves wave-like body motion, simultaneous overarm strokes, and a dolphin kick. It provides an intense core and upper body workout.
Health Benefits of Swimming
The science of swimming translates into several health benefits brought about by water resistance:
1. Muscular Strength and Endurance: The continuous resistance from water promotes muscle strength and endurance. Each stroke becomes a resistance workout, challenging various muscle groups.
2. Cardiovascular Fitness: Swimming is an effective aerobic exercise that improves heart health, lung capacity, and overall cardiorespiratory fitness.
3. Flexibility: The range of motion involved in swimming strokes enhances joint and muscle flexibility.
4. Low Impact: The buoyancy of water reduces impact on joints, making swimming an excellent exercise option for individuals with arthritis or injuries.
5. Calorie Burn: Water resistance means your body has to work harder, resulting in a high calorie burn. A vigorous swim can burn as many calories as running, but without the high-impact stress on the body.
6. Mental Health: The rhythmic nature of swimming and the sensory deprivation under water can have a calming effect, reducing stress and enhancing mental well-being.
Swimming, in essence, taps into the power of water to challenge your body in ways that no land exercise can match. It's a sport that merges the laws of physics with the marvel of human physiology to create a workout that is as effective as it is
enjoyable.
So, take the plunge into the exquisite science behind swimming. Let the water mould and shape you, challenging you, strengthening you, and propelling you towards a fitter, healthier self. Remember, every lap you swim is a testament to the amazing interplay of science and sport, a testament to your strength, your endurance, and your passion. Keep swimming, keep exploring, and let the water carve the best version of you!